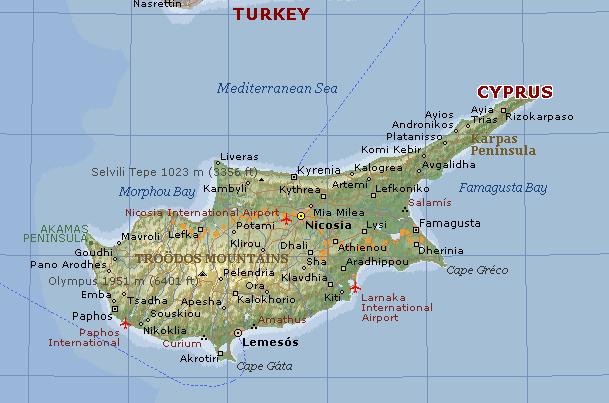
Cyprus, independent country and third largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Cyprus lies in the north-eastern part of the Mediterranean, about 65 km (40 mi) south of Turkey and 110 km (65 mi) west of Syria. Nicosia is the capital and largest city.
Steep, narrow mountains line the island’s northern coast, and an extensive mountain system rises in the south. At the center center of the island, between the mountains, lies the fertile Mesaoria plain, the site of Nicosia. Wide bays and small inlets indent the rocky coastline, which is broken in places by long, sandy beaches. Summers in Cyprus is hot and dry, and rain is scarce on the island, except during the winter months. Cyprus is vulnerable to drought, and most crops require irrigation.
Cyprus Population
| 1,226,573 | Current population |
| 626,471 | Current male population (51.1%) |
| 600,102 | Current female population (48.9%) |
Animal population
Terrestrial animals, Cyprus, 2018
| Species | Admin unit | Population | Units | Number of establishments | Units |
| Adult beef cattle | The Whole Country | 91 | Animals | 20 | Establishments |
| Adult dairy cattle | The Whole Country | 35909 | Animals | 325 | Establishments |
| Adult goats | The Whole Country | 165851 | Animals | 2005 | Establishments |
| Adult pigs | The Whole Country | 29165 | Animals | 53 | Establishments |
| Adult sheep | The Whole Country | 214754 | Animals | 1824 | Establishments |
| Backyard pigs | The Whole Country | 1555 | Animals | 199 | Establishments |
| Bees | The Whole Country | 51219 | Animals | 676 | Establishments |
| Broilers | The Whole Country | 10261056 | Animals | 78 | Establishments |
| Buffaloes | The Whole Country | 0 | Animals | 0 | Establishments |
| Calves | The Whole Country | 19727 | Animals | 306 | Establishments |
| Camelidae | The Whole Country | 103 | Animals | 5 | Establishments |
| Cattle | The Whole Country | 5 | Animals | Establishments | |
| Cervidae | The Whole Country | 167 | Animals | 7 | Establishments |
| Dogs | The Whole Country | 96978 | Animals | 72466 | Establishments |
| Domestic horses | The Whole Country | 1222 | Animals | 170 | Establishments |
| Donkeys/ Mules/ Hinnies | The Whole Country | 431 | Animals | 385 | Establishments |
| Equidae | The Whole Country | 4271 | Animals | 885 | Establishments |
| Fattening pigs | The Whole Country | 314780 | Animals | 50 | Establishments |
| Goats | The Whole Country | 93085 | Animals | 987 | Establishments |
| Kids | The Whole Country | 36658 | Animals | 1340 | Establishments |
| Lambs | The Whole Country | 42937 | Animals | 1318 | Establishments |
| Layers | The Whole Country | 551911 | Animals | 37 | Establishments |
| Male and female cattle | The Whole Country | 13400 | Animals | 311 | Establishments |
| Other commercial poultry | The Whole Country | 160666 | Animals | 16 | Establishments |
| Piglets | The Whole Country | 62652 | Animals | 48 | Establishments |
| Sheep | The Whole Country | 124197 | Animals | 796 | Establishments |
| Sheep/goats | The Whole Country | 242918 | Animals | 1065 | Establishments |
| Turkeys | The Whole Country | 31950 | Animals | 7 | Establishments |
Aquatic animals, Cyprus, 2018
| Species | Admin unit | Population | Units | Number of establishments | Units |
| Amphibians | The Whole Country | 0.00 | Animals | 0 | Establishments |
| Crustaceans | The Whole Country | 28.00 | Tones | 1 | Establishments |
| Fish | The Whole Country | 7390.00 | Tones | 15 | Establishments |
| Molluscs | The Whole Country | 0.00 | Tones | 0 | Establishments |
| Wild crustaceans | The Whole Country | 3.00 | Tones | Establishments | |
| Wild fish | The Whole Country | 1432.00 | Tones | Establishments | |
| Wild molluscs | The Whole Country | 35.00 | Tones | Establishments |
Agriculture & Livestock
Some 11 percent of the land area of Cyprus is under cultivation. Most of the holdings are small, and the vast majority of them are in the Turkish Cypriot sector.
The principal crops are potatoes, grapes, citrus fruits, cereals such as barley and wheat, carobs, and olives. The output of cereals and olives is insufficient to meet domestic demands, and Cyprus must import much of its food. Livestock breeding, mainly of sheep and goats, is important. Hogs, cattle (including draft oxen), donkeys (see ass), mules, and horses also are raised. Dairy products are mainly cheese and yogurt made from sheep and goat milk.
Livestock products, including poultry and milk, made up a significant part of the gross output by the value of the agricultural sector. In 1989 there were 49,000 cattle, 325,000 sheep, 208,000 goats, 281,000 pigs, and 2,475,000 chickens in the government-controlled area. During the 1980s, livestock production roughly doubled, as a result of subsidies, strict import regulations, and government-sponsored research that improved both the quality of livestock and its management. Although Greek Cypriots had become self-sufficient in pork and poultry, it was necessary to import beef, veal, and mutton to meet domestic needs. Specialists believed that the gradual lifting of import restrictions, as required by the EEC Customs Union Agreement, would put many inefficient breeders of livestock out of business.
Plants and Animals
The mouflon, a wild sheep, is native to the Mediterranean islands of Corsica, Sardinia, and Cyprus. The horns of the male can grow nearly into a full circle, distinguishing them from the female.
Forests of pine, cypress, and cedar cover about one-seventh of the total area of Cyprus, principally in the mountains. Other indigenous trees include juniper, plane, oak, olive, and carob. The eucalyptus, a tree that can thrive in warm, dry climates, has been planted extensively as a reforestation measure.
Cyprus has few large wild animals; the most notable of these, the mouflon, a wild sheep, is no longer common. Cyprus is home to foxes and fruit-eating bats. Birdlife is varied because the island is visited by migratory flocks. Among the prominent native birds are the griffon vulture and several varieties of partridge, especially francolin. Other game birds include snipe, quail, woodcock, and plover. Sea turtles live in coastal waters.
Resources
The chief natural resource of Cyprus is its arable land. The mountain soils tend to be peaty on higher flatlands but are shallow and stony on the slopes. Farming provides income for much of the population in the Turkish Cypriot north, although it is far less important in the Greek Cypriot south. The chief mineral resource is copper. Other minerals of significance include asbestos, pyrite, gypsum, and chromite. Mining has declined considerably in importance.
CYPRUS Delegate
Dr. Christodoulos Pipis
Acting Director
Veterinary Services
Ministry of Agriculture, Rural Development and Environment
1417 Athalassa
Nicosia
CYPRUS